BTK kinase is a member of the TEC kinase family and is a key regulator of the B-cell Receptor (BCR)-mediated signaling pathway. It is important for B-cell maturation, proliferation, survival and metastasis. Pharmacological inhibition of BTK is clinically effective against a variety of B-cell malignances, such as MCL, CLL, AML and ABC-DLBCL. MNK kinase is one of the key downstream regulators in the RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway and controls protein synthesis via regulating the activity of eIF4E. Inhibition of MNK activity has been observed to moderately inhibit the proliferation of AML cells.
After several years of extensive study, an international collaboration team including a group led by Dr. LIU Qingsong and Dr. LIU Jing at the High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CHMFL) and a group led by Dr. Nathanael Gray at Harvard Medical School through a structure-based drug design approach has successfully developed the first highly potent and relatively selective dual BTK/MNK inhibitor as a potential drug candidate for B-Cell malignancies.
Given the fact that BTK kinase-mediated BCR signaling cross talks with PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and MNK kinase-mediated eIF4E signaling is downstream of RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK as well as PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling, the researchers hypothesized that simultaneously inhibiting BTK and MNKs kinases would exert combinatorial efficacies than targeting these kinases individually.
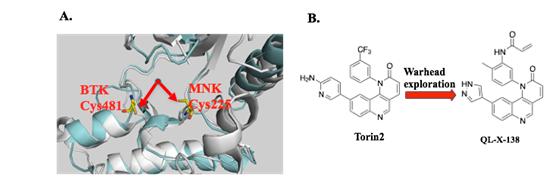
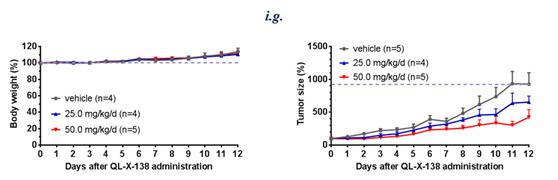
Based on inspection of the available X-ray structures of BTK and MNK1/2 kinases, the team has successfully developed the first highly potent and relatively selective dual BTK/MNK inhibitor by employing structure-based drug design strategy. Simultaneous inhibition of BTK and MNK kinase activity shows greater efficacy in the cell lines with moderate sensitivity to selective BTK inhibitors. In addition, in the SKM-1 cell inoculated xenograft mouse model, QL-X-138 displayed a dose-dependent tumor inhibition activity.
The rational design of multiple targeted drugs is usually challenging considering the difficulty of achieving a high level of selectivity, however it is an attractive approach to achieve improved efficacy against oncogene-driven diseases. This study again exemplifies that it is feasible to achieve a selective multiple targeted inhibitor through a rational design approach.
The study was supported by the “Thousand Talents Program”, “Hundred Talents Program” of The Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Anhui Province Natural Science Foundation Annual Key Program, et al.
The results were published in the online journal: Leukemia (doi:10.1038/ leu.2015. 180), entitled “Discovery of a BTK/MNK dual inhibitor for lymphoma and leukemia”.
|
|
|
Illustration of the rational design concept in X-ray structure of BTK and MNK kinase |
|
|
|
QL-X-138’s anti-tumor effects on SKM-1 inoculated mouse model |