Oct 16,2017|By
A research team led by Prof. LIN Wenchu from High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CHMFL) has revealed that combination treatment of two small molecules (BEZ235 and RAD001) effectively kill small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells. Their findings have been published online in Oncotarget.
SCLC is the most aggressive subtype of lung cancer accounting for 10~15% of the total lung cancer cases. SCLC differs from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in having neuroendocrine differentiation, higher proliferation index and a tendency to metastasize earlier.
However, there is no targeted therapy being clinically approved for the treatment of SCLC so far.
By mining the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) database, Dr. HONG Bo and his coworkers of LIN’s team found that PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway was aberrant in 92% of SCLC cell lines.
Through the study, they found that combination of RAD001 (mTOR inhibitor) and BEZ235 (PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor) synergistically inhibited the growth of SCLC cells.
Moreover, mechanistic study indicated that such a combination dramatically inhibited the activation of AKT as well as strongly reduced the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and its downstream target Mcl-1.
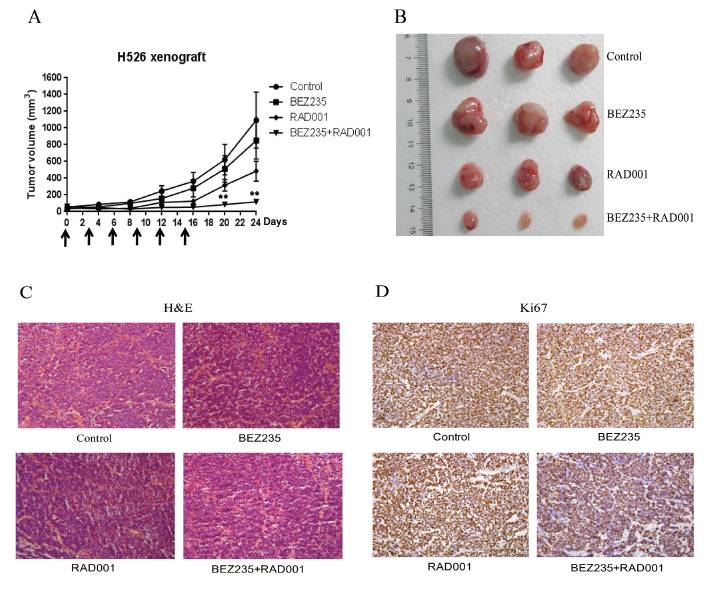
Furthermore, in vivo mice study demonstrated that the combination treatment suppressed tumor growth by 89.3% relative to control treatment.
Interestingly, they found that the phosphorylation level of 4E-BP1 was significantly correlated with SCLC sensitivity to RAD001 and BEZ235.
In summary, this study suggests that combination of BEZ235 and RAD001 may be an effective regimen for SCLC treatment, and p-4E-BP1 may serve as a predictive biomarker for SCLC response to mTOR inhibitor.
This investigation was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, and the 100-Talent Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
 |
|
BEZ235/RAD001 combination remarkablely inhibits SCLC tumor growth in vivo: (A) Combination treatment with BEZ235 and RAD001 significantly induced growth inhibition of SCLC xenograft, (B)Imaging of representative tumors from each group, (C) H&E staining and (D) Immunohistochemical detection of Ki67 |
Attachments Download: