May 29,2012|By
The substitution effect is of great importance in the study of the superconducting mechanism of the iron-based high temperature superconductors. It is known that the 3d electrons of Fe ion are responsible for the superconductivity in iron-based superconductors. The question is, what is the consequence of superconductivity and other physical properties if one substitutes at the Fe-site by using other transition-metal elements?
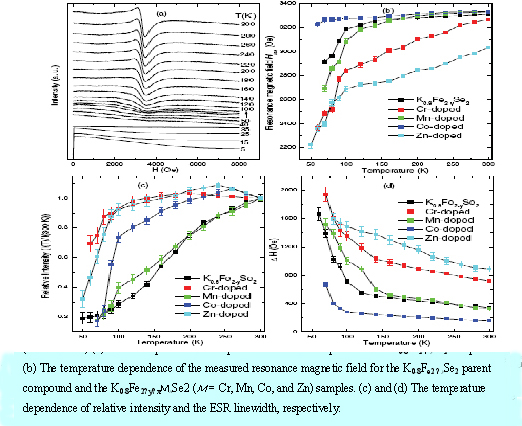
Researchers from University of Science and Technology of China and High Magnetic Field Laboratory of Chinese Academy of Sciences studied the response of superconductivity and magnetic properties on the transition-metal dopants in K.0.8Fe2-ySe2 superconductor. They find that the introduction of Cr, Co, and Zn leads to severe depression of superconductivity, while the superconducting transition temperature keeps nearly unchanged in Mn-doped samples. Through electron-spin-resonance study, they find that introduction of Cr, Co, and Zn induces local magnetic moments into the system, which leads to the magnetic pair-breaking effects. On the other hand, the magnetic properties of the Mn-doped samples are similar to the parent sample. This result gives crucial evidence that the magnetic pair-breaking effect is response for the suppression of superconductivity in this system. This work was published on Physical Review B , 84,014502(2011).
Attachments Download: