A Chinese joint team reported the synthesis of metal-free multifunctional therapeutic reagents by a one-step hydrothermal method using formamide as carbon and nitrogen source.
The research team was led by Prf. WANG Hui and Prof. LIN Wenchu from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science.
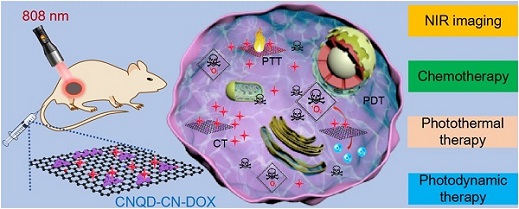
Metal-free multifunctional nanomaterials have broad application prospects in the integrated cancer diagnosis and treatment.
"The combination of graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and two-dimensional carbon-based nanomaterials might be a potential candidate for realize imaging-guided cancer synergistic therapy due to its excellent performance including optical properties, efficient light-to-heat conversion capability, and NIR-induced singlet oxygen generation. " WANG Hui said, who designed the project.
"However, several disadvantages are associated with the synthesis of related nanocomposite, including multiple reaction precursors, complex synthesis processes, potential weak interaction, which produce large amounts of waste and limit their scalable production and reproducibility." he then explained.
Prof. WANG Hui, who did design and analysis work of their materials preparation introduced, "We reported a type of metal-free multifunctional nanoplatform based on graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots embedded in carbon nanosheets (CNQD-CN) by one-step hydrothermal treatment using an organic solvent (formamide). "
Prof. LIN Wenchu further elaborated, "The CNQD-CN can be utilized as a NIR/pH dual-responsive drug delivery system to improve response to chemotherapy. In addition, the CNQD-CN possesses both light-to-heat conversion and singlet oxygen generation capabilities under a single NIR excitation wavelength for combined photodynamic and photothermal therapy."
Ph.D. candidate LIU Hongji, Graduate students LV Xiaotong and Associate Professor QIAN Junchao who are the young scientists in that study team, are the first authors of this paper.
The study was sponsored by NSFC, the start-up fund of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Program of Hefei Science Center of CAS, Science and Technology Major Project of Anhui Province, Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Materials and Energy Conservation of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Key Laboratory of High Magnetic Field and Ion Beam Physical Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Anhui Key Laboratory of Modern Biomanufacturing. A portion of this work was supported by the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of Anhui Province.
Cartoon of CNQD-CN for NIR imaging and combined chemotherapy and phototherapy of cancer (Image by LIU Hongji)