Apr 08,2014|By
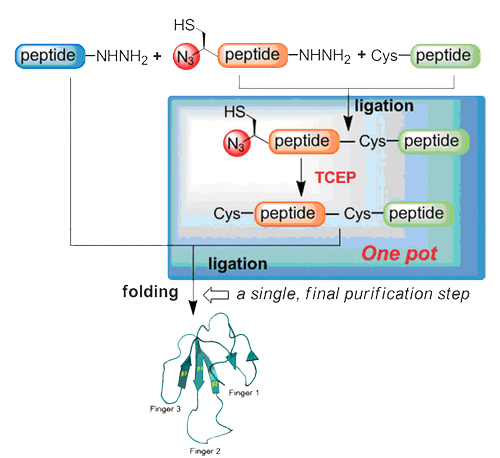
An efficient one-pot chemical synthesis of snake venom toxin Mambalgin-1 was achieved using an azide-switch strategy combined with hydrazide-based native chemical ligation. Synthetic Mambalgin-1 exhibited a well-defined structure after sequential folding in vitro. NMR spectroscopy revealed a three-finger toxin family structure, and the synthetic toxin inhibited human acid-sensing ion channel 1a.
Related links to this article: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2014/cc/c4cc00779d
Attachments Download: